CAR T-cell therapy is a well-known and cutting-edge cancer treatment option. It is a groundbreaking immunotherapy that uses a patient’s own immune system to treat cancer. CAR-T cell therapy has demonstrated remarkable success in treating certain types of leukaemia and lymphoma, giving patients with previously untreatable or relapsed cancers new hope.
We will learn about the current status and future prospects of CAR T- Cell therapy in Pediatric Oncology in this blog.
What is CAR T-Cell therapy?
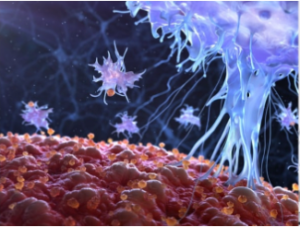
CAR T-cell therapy, also known as Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy, is a revolutionary form of immunotherapy that has transformed cancer treatment. It is a personalised and targeted approach that uses the power of a patient’s own immune system to effectively fight cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy has demonstrated remarkable success in treating certain types of leukaemia and lymphoma, giving patients with previously untreatable or relapsed cancers new hope.
CAR T-cell therapy has demonstrated remarkable efficacy, particularly in the treatment of B-cell malignancies such as B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). CAR T-cell therapy has resulted in complete remission or long-term disease control in some patients who were unresponsive to standard treatments or had a poor prognosis.
CAR T-cell therapy research and development continue to expand, with ongoing studies investigating its potential in treating other types of cancer and solid tumors. Efforts are also being made to improve the persistence and durability of CAR T-cell responses in order to control cancer for the long term.
Steps involved in CAR T-Cell treatment process
CAR T-cell therapy entails several complex steps that are critical to its success in cancer treatment. The procedure is highly personalized, with T cells from each patient genetically modified to target specific cancer antigens. The following are the steps in CAR T-cell therapy:
Patient Eligibility and Evaluation
The first step entails a thorough examination of the patient’s medical history, cancer type, and overall health. CAR T-cell therapy is not appropriate for all patients, and careful selection is required to ensure safety and efficacy. Patients with specific types of leukaemia or lymphoma who have not responded or relapsed to standard treatments may be candidates for CAR T-cell therapy.
T Cell Collection (Leukapheresis)
If the patient is found to be eligible, the next step is to collect T cells from their blood using a technique known as leukapheresis. The patient’s blood is drawn through a specialised machine that separates the T cells from the rest of the blood components during leukapheresis. T cells are collected and then sent to a laboratory for genetic modification.
T Cell Genetic Engineering
T cells are genetically engineered in the laboratory to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on their surface. CARs are synthetic receptors that recognize specific antigens on cancer cells. CARs are built with a combination of genetic materials, including antibodies and signalling molecules, to allow T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
CAR-T Cell Expansion and Culturing
CAR-T cells are expanded and cultured in the laboratory after being genetically modified. This step ensures that there are enough CAR-T cells available for reinfusion into the patient’s body. To achieve the desired cell count, the culturing process may take several days.
Conditioning Chemotherapy
Patients receive conditioning chemotherapy prior to CAR-T cell infusion. This chemotherapy is designed to suppress the patient’s natural immune system and create a more favourable environment for CAR-T cells to thrive and function properly. The conditioning regimen also reduces the possibility of the patient’s immune system attacking the CAR-T cells.
CAR-T Cell Infusion
The CAR-T cells are ready for infusion once they have been expanded and the patient has completed the conditioning chemotherapy. The CAR-T cells are given to the patient intravenously, much like a blood transfusion. The infused CAR-T cells then circulate throughout the body, seeking out cancer cells based on the antigens they have been programmed to recognize.
CAR-T Cell Activation and Cancer Cell Destruction
Once inside the patient’s body, CAR-T cells activate when they come into contact with cancer cells expressing the targeted antigens. The CARs on T cells’ surfaces recognize and bind to cancer cells, triggering an immune response. This activation causes cancer cells to be destroyed, resulting in tumor reduction and potential remission.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Patients are closely monitored after CAR-T cell infusion for potential side effects such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic toxicities. Follow-up visits and imaging tests are performed on a regular basis to assess treatment response and disease progression. Long-term monitoring is essential for determining the long-term viability of CAR-T cell therapy and its impact on cancer control.

CAR T-cell therapy has shown remarkable success in Pediatric oncology, providing new hope for young patients with cancers that have been difficult to treat with traditional therapies. CAR T-cell therapy is currently being used in pediatric oncology to treat specific types of pediatric cancers, particularly B-cell malignancies.
It is important to note that CAR T-cell therapy is currently approved in pediatric oncology for specific indications, primarily the treatment of B-cell malignancies. However, ongoing research and clinical trials continue to investigate its potential in other types of pediatric cancers.
CAR T-cell therapy’s success in pediatric oncology can be attributed to its targeted approach, in which genetically modified T cells recognize and attack cancer cells while sparing healthy cells. This personalized treatment has shown remarkable outcomes in patients who had limited treatment options and faced poor prognosis.
Some of the Pediatric Cancers treated with CAR-T Cell therapy are:
- B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL): The most common type of childhood leukaemia, B-ALL is distinguished by the overproduction of immature B-cell lymphocytes. CAR T-cell therapy has shown promising results in treating relapsed or refractory B-ALL, where conventional therapies have failed. Clinical trials and real-world studies have shown that CAR T-cell therapy results in high remission rates and long-term disease control in pediatric patients with B-ALL.
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma that can affect children and adolescents. For pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, CAR T-cell therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option. In this difficult patient population, the therapy has shown significant efficacy in achieving remissions and extending survival.
- PMBCL (Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma): PMBCL is a rare non-Hodgkin lymphoma that primarily affects adolescents and young adults. CAR T-cell therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of relapsed or refractory PMBCL, providing a new treatment option for patients with limited therapeutic option
- Neuroblastoma: it is a type of cancer that develops from immature nerve cells and commonly affects young children. While CAR T-cell therapy is not yet approved for the treatment of neuroblastoma, ongoing preclinical research and clinical trials are looking into its potential use in this difficult pediatric cancer.
Challenges faced by International patients in accessing CAR-T Cell therapy
When it comes to CAR-T cell therapy from the United States, international patients face a number of challenges. Despite the fact that this groundbreaking treatment has the potential to save lives, these obstacles may prevent them from benefiting from it. Among the major challenges are:
Cost of Treatment: Because CAR-T cell therapy is a highly advanced and personalised treatment, it can be costly. The price includes T cell collection and genetic modification, CAR-T cell manufacturing, hospitalisation, monitoring, and post-treatment care. For international patients, the cost of travel, lodging, and other expenses adds to the financial burden.
Insurance Coverage: Insurance coverage for CAR-T cell therapy varies greatly between countries. Some international patients may have difficulty obtaining treatment approval or may be required to travel.
Logistics and travel: Travelling to another country for CAR-T cell therapy presents logistical challenges, such as obtaining visas, arranging travel accommodations, and navigating the healthcare system in an unfamiliar environment. Language barriers may also make communicating with healthcare providers more difficult.
Timing and Access: The availability of CAR-T cell therapy varies by country and hospital or treatment centre. International patients may face long wait times or limited access to clinical trials and approved treatments, potentially delaying treatment.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Regulations and approval processes for CAR-T cell therapy vary by country. When trying to access treatment in the United States, international patients may face regulatory challenges, such as obtaining approval for the exportation of their T cells, complying with local regulations, and navigating cross-border healthcare logistics.
Pre-Treatment Evaluation: Before starting CAR-T cell therapy, patients must go through a thorough evaluation to determine eligibility and assess potential risks. International patients may face difficulties in coordinating pre-treatment evaluations and sharing medical records and test results with the treatment centre in the United States.
Post-Treatment Monitoring: To manage potential side effects and assess treatment response, CAR-T cell therapy necessitates careful monitoring and follow-up. International patients may have difficulty arranging post-treatment follow-up visits and long-term care, both of which are critical for successful treatment outcomes.
Support System: During their treatment journey in the United States, international patients may be without a local support system. Emotional and practical support from family and friends can be critical for patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy, particularly if they are far from home.
CAR-T Cell therapy through MediPocket USA
To help international patients overcome these obstacles, medical facilitation companies such as MediPocket USA play an important role. MediPocket USA assist patients in navigating the complexities of CAR-T cell therapy access by providing logistical support, coordinating medical evaluations, guiding patients through the treatment process, and ensuring seamless communication between the patient, the U.S. treatment centre, and healthcare providers in the patient’s home country.
In Conclusion
To summarize, CAR-T cell therapy is a remarkable and revolutionary treatment for pediatric cancer, providing new hope for young patients with otherwise difficult and refractory cancers. Its personalized approach, which harnesses the power of the patient’s immune system, has shown exceptional success in treating specific types of pediatric cancers, particularly B-cell malignancies such as B-ALL and DLBCL.
Despite its proven efficacy, CAR-T cell therapy is still limited to a few treatment centers, mostly in the United States, making it inaccessible to many patients around the world. This is where MediPocket USA comes in, bridging the gap between patients and cutting-edge treatments like CAR-T cell therapy.
MediPocket USA serves as a cross-border company, assisting international patients in gaining access to CAR-T cell therapy and other high-end treatments in the United States. MediPocket USA ensures that international patients have access to phenomenal CAR-T cell therapy and other cutting-edge treatments that were previously unavailable due to their expertise in navigating the complexities of cross-border healthcare.