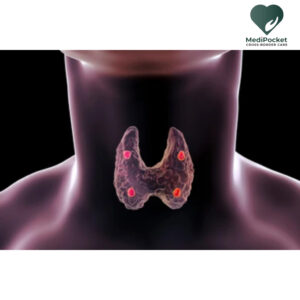
The parathyroid gland are tiny endocrine glands found near the thyroid gland in the neck. The majority of people have four parathyroid glands, however some have fewer or more. The parathyroid glands are in charge of manufacturing and secreting parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium levels in the body.
Thyroid hormone regulates calcium levels by increasing the release of calcium from bones into the circulation, increasing calcium absorption from the intestines, and decreasing calcium excretion by the kidneys. When calcium levels in the blood are too low, the parathyroid glands produce more PTH, which aids in calcium replenishment. When calcium levels are excessively high, the parathyroid glands produce less PTH, which aids in calcium regulation.
A complicated feedback mechanism involving calcium levels in the blood, vitamin D levels, and other hormones regulates the parathyroid glands. When calcium levels go too low, the parathyroid glands produce PTH. When calcium levels get too high, the parathyroid glands are unable to produce PTH.
Dysfunction of the parathyroid glands can result in abnormal calcium levels in the blood, which can cause a variety of symptoms and health issues. Hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid glands), hypoparathyroidism (underactive parathyroid glands), and parathyroid malignancy are all prevalent parathyroid illnesses. A multitude of variables, including heredity, autoimmune illnesses, and specific drugs, can cause these problems.
Types of parathyroid gland
The human body has four parathyroid glands, all of which are situated near the thyroid gland in the neck. The four parathyroid glands are normally split into two groups: superior and lower parathyroid glands. Further information on each variety of parathyroid gland may be found below:
- Superior parathyroid glands: These glands are found above the thyroid gland, towards the bottom margin of the thyroid cartilage. These glands are normally found beneath the thyroid gland, but their location varies from person to person.
- Inferior parathyroid glands: These glands are found beneath the thyroid gland, near the thymus gland. These glands are frequently found behind the thyroid gland’s lower poles.
It’s worth mentioning that, while most individuals have four parathyroid glands, some people may have more or less. Some persons may have one or more “ectopic” parathyroid glands positioned elsewhere in the neck or chest. These ectopic glands can occasionally cause parathyroid problems such as hyperparathyroidism.
Regardless of the number or location of the parathyroid glands, they all perform the same function: generating and secreting parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium levels in the body. Dysfunction of the parathyroid glands can result in abnormal calcium levels in the blood, which can cause a variety of symptoms and health concerns.
Disorders of parathyroid gland
There are various conditions that can impair parathyroid gland function, including:
Hyperparathyroidism
It is a disorder in which one or more parathyroid glands release an excessive amount of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Hypercalcemia (excess calcium in the blood) might result, causing a variety of symptoms such as weariness, weakness, bone pain, kidney stones, and excessive urination. The most frequent form of the illness is primary hyperparathyroidism, which arises when one of the parathyroid glands produces a noncancerous tumor.
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism occurs when the parathyroid glands do not generate enough parathyroid hormone (PTH). This might result in unusually low calcium levels in the blood (hypocalcemia), causing muscular cramps, twitching, seizures, and other neurological symptoms. Hypoparathyroidism can be caused by a variety of reasons, including surgery-related injury to the parathyroid glands, autoimmune illnesses, and genetic abnormalities.
Parathyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is an uncommon kind of cancer that affects the parathyroid glands. It can cause the glands to release excessive amounts of PTH, resulting in hypercalcemia and other symptoms. Surgery and, in certain situations, radiation therapy or chemotherapy are used to treat parathyroid cancer.
Parathyroid adenoma
A benign tumor that forms on one of the parathyroid glands, leading it to generate an excessive amount of PTH. This can result in hypercalcemia and other hyperparathyroid symptoms. Surgery to remove the afflicted gland is commonly used to treat parathyroid adenomas.
Parathyroid hyperplasia
It is a disorder in which all four parathyroid glands expand and generate excessive PTH. This can result in hypercalcemia and other hyperparathyroid symptoms. Surgery to remove part or all of the afflicted glands is commonly used to treat parathyroid hyperplasia.
Symptoms
Depending on whether the glands produce too much or too little parathyroid hormone (PTH), as well as the degree and duration of the condition, the symptoms of parathyroid gland problems might vary. The following are some frequent symptoms of parathyroid gland disorders:
Hyperparathyroidism (parathyroid glands that are overactive):
- increased thirst and urine
- Weakness and fatigue
- Pain in the joints and bones
- Stones in the kidney
- Bone fractures or osteoporosis
- Constipation or abdominal discomfort
- Depressive symptoms or forgetfulness
Hypoparathyroidism (parathyroid glands that are underactive):
- Hand, foot, or face tingling, numbness, or cramping
- twitching or spasming muscles
- Weakness and fatigue
- Skin or hair that is dry or coarse
- deterioration or loss of teeth
- Atypical heart beat
Parathyroid cancer
- Breathing or swallowing difficult
- Voice changes or hoarseness
- Neck discomfort or edema
- Neck lymph nodes enlargement
It’s worth noting that many people with parathyroid gland abnormalities have no symptoms or just have modest symptoms that go undiagnosed.
The United States is the finest destination to obtain treatment for any condition. Advanced technology and well-trained doctors are the finest in their profession, resulting in early diagnosis and appropriate treatment for the patient. As a result, Medipocket World electronically connects US doctors with Indian patients. We aspire to give top healthcare to all Indian patients while striving for perfection in treatment and diagnosis. Register today to reserve a consultation with an American board-certified endocrinologist.